OPERATING SYSTEM MCQ BASED QUESTION
(Multi Choice Question)
This Blog cover all possible Multi Choice Question from topic operating system, type of operating system, process, synchronization , dead lock, memory management
Total amount of question covers in This MCQ series is 100. They cover all the important aspect related to that topic provided below.
If you want the Hard copy of MCQ then u can comment in the comment session. The Question is prepared after putting lot of effort so instead of copy it please share the Link so that we can able to take Benefit of our effort.
Q1 Operating System means
a) A Set of programs which control computer working
b) A way of managing resources
c) it work like a interface between user and Hardware
d) All of the Above
Sol: All of the above
Q2 The Primary job of an operating system is to:
a) Command Resources
b) Manage Resources
c) Provide utilities
d) Be user Friendly
Sol: Manage Resources
Q3 When a computer is ON then its OS software has to reside in
a) Primary Storage
b) Main Storage
c) AUX Storage
d) None of the above
Sol. Primary Storage
Q4 Two Basic types of Operating System are
a) Batch and Time Sharing
b) Sequential and Real Time
c) Direct and interactive
d) Batch and interactive
Sol: Batch and Time Sharing
Q5 A computer is a combination of
a) Computer Hardware + Software
b) Hardware + Software + Processes
c) Computer Hardware + Operating System
d) None of the Above
Sol. Computer Hardware + Operating System
Q6 SPOOLING stand for
a) Simultaneous Peripheral Operation Online
b) Simple Peripheral Operation Online
c) Simultaneous Printing Operation Online
d) None of the Above
Sol. Simultaneous Peripheral Operation Online
Q7 Which of the following is not the example of operating system
a) DOS
b) Window
c) Mach
d) All of them are Operating System
Sol. All of them are Operating System
Q8 The Process of transferring Data intended for a peripheral device onto a disk for some period of time is known as
a) Multi Programming
b) Spooling
c) Caching
d) None of the above
Sol. Spooling
Q9 An Operating system is
a) Application Software
b) System Software
c) AI program
d) None of the above
Sol. System Software
Q10 To access the services of operating system, the interface is provided by the
a) System calls
b) API
c) Library
d) Assembly instructions
Sol. System calls
Q11) Which of the following is not an operating system?
a) ULTRiX
b) AIX
c) Oracle
d) Rhapsody
Sol. Oracle
Q12 When was the first operating system developed?
a) 1946
b) 1942
c) 1950
d) 1958
Sol. 1950
Q13 A Shell is a
a) Hardware Component
b) Command Interpreter
c) Kernel
d) None of the above
Sol. Command Interpreter
Q14 Which of the following not a Operating System layer
a) Kernel
b) Shell
c) Application
d) Critical Section
Sol. Critical Section
Q15 BIOS is used?
a) By compiler
b) By operating system
c) By application software
d) By interpreter
Sol. By operating system
Q16 Which one of the following is not true?
a) kernel is the central core of the operating system
b) During booting, kernel is the first part of operating system to load into memory
c) kernel is made of various modules which can not be loaded in running operating system
d) kernel remains in the memory during the entire Execution
Sol. kernel is made of various modules which can not be loaded in running operating system
Q17 What is the main function of the command interpreter?
a) to get and execute the next user-specified command
b) to provide the interface between the application and Hardware
c) to handle the files Request
d) none of the above
Sol. to get and execute the next user-specified command
Q18 A Small Program Which Load OS into the memory is called as
a) ROM
b) BIOS
c) Boot Strap Loader
d) None of the above
Sol. Boot Strap Loader
Q19 Which of the Open-source operating system?
a) UNIX Operating System
b) Windows Operating system
c) Linux Operating system
d) None of these
Sol. UNIX Operating System
Q20 In Soft Real Time System data files are
a) Small
b) Medium
c) Large
d) None of the Above
Sol. Medium
Q21 Which of the following is an Example of Real time OS
a) UNIX
b) MARUTI
c) WIN-NT
d) None of the above
Sol. MARUTI
Q22 An Example of Network Operating System
a) BSD
b) Harmony
c) MS-DOS
d) None of the above
Sol. BSD
Q23 What is the advantage of layered approach to the design of Operating System
a) It simplifies the construction and debugging
b)A modification made in a particular layer will not affect the other layers.
c) The hardware layer is the innermost layer So a user cannot directly modify or access it
d) All of the above
Sol. All of the above
Q24 Reason behind dual mode operation of processors?
a) Dual-mode operation is used to provide protection & security to the user’s program.
b) If you do not have Dual-mode, then you can write over the Operating System.
c) The Operating System gains the main control of the computer in the kernel mode.
d) All of the above
Sol. All of the above
Q25 Which of the following is type of Kernel
a) monolithic kernel
b) hybrid kernel
c) microkernel
d) All of the above
Sol. All of the above
Q26 The Term Process was coined by
a) Barry Boehm
b) Daley
c) Albrecht
d) None of the above
Sol. Daley
Q27 One can interact with an Operating System by mean of
a) System commands
b) System Call
c) Both a and b
d) None of the above
Sol. Both a and b
Q28 PCB stands for
a) Process common block
b) Process control Block
c) Process care Block
d) None of the above
Sol. Process control Block
Q29 The size of WIN-NT OS is above 1,60,000 LOC While WIN-2000 has size of
a) 1,19,00,000 LOC
b) 2,60,00,000 LOC
c) 3,25,00,000 LOC
d) None of the above
Sol.3,25,00,000 LOC
Q30 A process can be terminated due to __________
a) normal exit
b) Occurrence of Fault
c) killed by another process
d) all of the Above
Sol. All of the Above
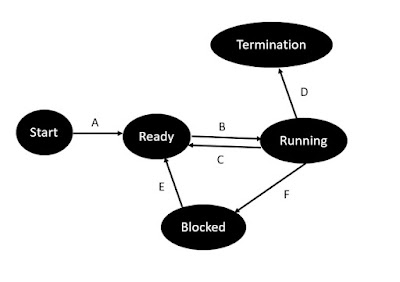
Q31 What is the ready state of a process?
a) when process is ready scheduled
b) when process is unable to run until some IO has been completed
c) when process is executing in the CPU
d) none of the mentioned
Sol. when process is ready scheduled
Q32 In Unix, Which system call creates the new process?
a) fork
b) create
c) new
d) none of the mentioned
Sol. Fork
Q33 Which of the following is true about shell?
a) Term “terminal” is synonymous to shell
b) Bash is synonymous to shell
c) Shells are ought to be part of the operating system
d) Users can install third party shells to replace ones shipped with OS if any
Sol. Users can install third party shells to replace ones shipped with OS if any
Q34 Which of the following is abstracted by operating system?
a) Processor
b) Memory
c) Network Cards
d) All of the above
Sol. All of the above
Q35 Which of the following are valid differences between CreateProcess() and fork():
a) fork() by default creates a child process with same file descriptors while CreateProcess() does not.
b) CreateProcess() by default creates a child process with same file descriptors while fork() does not.
c) fork() duplicates the program for different process. CreateProcess() creates different process with new program.
d) CreateProcess() does not return the pid of the child process to the parent process while fork()
returns the child process pid to parent process.
e) CreateProcess() is more efficient than fork() then exec() without copy-on-write.
Sol.
a) fork() by default creates a child process with same file descriptors while CreateProcess() does not.
c) fork() duplicates the program for different process. CreateProcess() creates different process with new program.
e) CreateProcess() is more efficient than fork() then exec() without copy-on-write.
Q36 Which system call returns the process identifier of a terminated child?
a) wait
b) exit
c) fork
d) get
Sol. Wait
Q37 The address of the next instruction to be executed is provided by
a) CPU registers
b) program counter
c) process stack
d) pipe
Sol. Program Counter
Q 38 When the process want to perform I/O operation
a) It is placed in an termination state
b) It is placed in a waiting state
c) It is placed in the ready state
d) None of the above
Sol. It is placed in a waiting queue
Q39 Long-term scheduler is responsible for?
a) selecting which process has to be brought into the ready queue
b) selecting which process has to be executed next
c) selecting which process to remove from memory by swapping
d) None of these
Sol. selecting which process has to be brought into the ready queue
Q 40 Medium-term scheduler is responsible for ?
a) selecting which process has to be brought into the ready queue
b) selecting which process has to be executed next
c) selecting which process to remove from memory by swapping
d) None of these
Sol. selecting which process to remove from memory by swapping
Q41 Short-term scheduler is responsible for?
a) selecting which process has to be brought into the ready queue
b) selecting which process has to be executed next
c) selecting which process to remove from memory by swapping
d) None of these
Sol. selecting which process has to be executed next
Q42 The primary distinction between the short term scheduler and the long term scheduler is
a) The length of their queues
c) The type of processes they schedule
d) The frequency of their execution
e) None of these
Sol. The frequency of their execution
Q 43 Which of the following is responsible for context switching
a) short term scheduler
b) long term scheduler
c) Dispatcher
d) medium-term scheduler
Sol. Dispatcher
Q44 PCB is
a) Data Structure
b) Command
c) Controlling of process
d) None of the above
Sol. Data Structure
Q45 In Which mode of execution the control is taken form the process force fully
a) Preemptive Mode
b) Non Preemptive Mode
c) in both Preemptive Mode and Non Preemptive Mode
d) None of the above
Sol. Preemptive Mode
Q46 In a time-sharing operating system, when the time slot given to a process is completed, the
process goes from the running state to the
a) Blocked state
b) Ready state
c) Suspended state
d) Terminated state
Sol. Ready state
Q47 CPU bound Process Spend most of the time in
a) CPU
b) Input / Output
c) block state
d) None of the above
Sol. CPU
Q48 In a multi-programming environment
a) the processor executes more than one process at a time
b) the programs are developed by more than one person
c) more than one process resides in the memory
d) a single user can execute many programs at the same time
Sol. the processor executes more than one process at a time
Q49 Each process has their own process control block
a) True
b) False
Sol. True
Q50 Suppose that a process is in “Blocked” state waiting for some I/O service. When the service is completed, it goes to the
a) Running state
b) Ready state
c) Suspended state
d) Terminated state
Sol. Ready state
Q51 Consider a system with n CPU processor then What is maximum and minimum number of process the may be reside ready , running and block state
a) Ready: min=0 & max=n-1 ,Running: min=0 & max=n, Ready: min=0 & max=all
b) Ready: min=0 & max=all ,Running: min=0 & max=n, Ready: min=0 & max=all
c) Ready: min=0 & max=all ,Running: min=0 & max=all, Ready: min=0 & max=all
d) Ready: min=all & max=all ,Running: min=0 & max=n, Ready: min=0 & max=all
Sol. b) Ready: min=0 & max=all ,Running: min=0 & max=n, Ready: min=0 & max=all
Q52.Which section comprises the compiled program code, read in from non-volatile storage when the program is launched.
a) text section
b) data section
c) heap
d) stack
Sol. Text Section
Q53 ____ section is dynamically allocated memory to a process during its run time
a) text section
b) data section
c) heap
d) stack
Sol. Heap
Q54 which contains temporary data for process (such as function parameters, return addresses, and local variables)
a) text section
b) data section
c) heap
d) stack
Sol. stack
Q55 Process control block (PCB) consist of
a) list of open Registers
b) process state
c) process id
d) All of the above
Sol. All of the above
Q56
Which is True
a) Round Robin
b) First-In First-Out
c) Multilevel Queue Scheduling
d) Multilevel Queue Scheduling with Feedback
Sol. First-In First-Out
Q72 Which of the following does not interrupt a running process?
a) A device
b) Timer
c) Scheduler process
d) Power failure
Sol. Scheduler process
Q73 Where does the swap space reside ?
a) RAM
b) Disk
c) ROM
d) On-chip cache
Sol. Disk
Q74 Which of the following need not necessarily be saved on a context switch between processes?
a) General purpose registers
b) Translation look-aside buffer
c) Program counter
d) All of the above
Sol. Translation look-aside buffer
Q75 What is the swap space in the disk used for?
a) Saving temporary html pages
b) Saving process data
c) Storing the super-block
d) Storing device drivers
Sol. Saving process data
Q76 The objective of multi programming is
1. to have more than one process running at all times.
2. to have single process run at a time
3. to achieve maximum CPU utilization
4. to achieve minimize CPU utilization
a) 1,2
b) 1,3
c) 2,3
d) 2,4
Sol. 1,3
Q77 In single-processor system
1. it never support more than one running process at a time
2. if more than one processes, one process execute at a time rest will wait until the CPU is free.
3. the CPU utilization can be maximize
4. there more than one process can run in CPU
a) 1,3
b) 1,2
c) 2,3
d) 2,4
Sol. 1,2
Q 78 The ready queue is generally stored as a______
a) Array
b) Stack
c) Linked List
d) None of the above
Sol. Linked List
Q 79 Once the process is allocated the CPU and is executing, which of several events could occur:
1. The process can perform an I/O request and can be placed in waiting queue
2. The process can able to create a new child process and wait for the child’s termination.
3. The process could be removed forcibly from the CPU can be put back in ready queue, due to interrupts, due to incoming of higher priority process, due to time stamp
b) turnaround time
c) response time
d) throughput
Sol. Long Term Scheduler
Sol. Short Term Scheduler
a) job queue
b) ready queue
c) execution queue
d) process queue
a) shortest job scheduling
b) round robin scheduling
c) priority scheduling
d) multilevel queue scheduling
Sol. OS is independent of the hardware on which it executes
Q97 State True or False for the question related to system calls. An OS designer who is designing a network stack,
1. Exposes, to the User, the details of the protocol used to send the data.
2. Exposes, to the User, the interface to set the protocol used for sending the data.
a) 1- False 2 – True
b) 1- True 2- False
c) 1 – True 2-True
d) 1-False 2-False
Sol. 1- False 2 – True
Q98 State True or False. In the absence of system calls, a user process can never access the memory allocated to kernel processes.
- True
- False
|
PNO |
AT |
BT |
CT |
TAT |
WT |
|
P0 |
0 |
9 |
13 |
13 |
4 |
|
P1 |
1 |
4 |
5 |
4 |
0 |
|
P2 |
2 |
9 |
22 |
20 |
11 |
So Avg Waiting Time is (4+0+11)/3=5
For More Question Visit the Provided Below
OPERATING SYSTEM 999+ MCQ BASED Most Important QUESTION WITH ANSWER Part 2